Cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide. According to calculations by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2020 almost 10 million deaths were attributed to this disease, almost one in six of those registered.
The term is used generically to designate a broad group of diseases that can affect any part of the body. A defining characteristic of cancer is the rapid multiplication of abnormal cells. For example, when cancer starts in the prostate, it is called prostate cancer.
This uncontrolled growth can be limited to a specific area or extend beyond its usual limits, invading adjacent parts of the body or spreading to other organs. This is a process known to all and called metastasis.
The most common types of cancer are breast, lung, colon and rectum, and prostate. According to the Spanish Association Against Cancer (AECC), prostate cancer is the most common tumor in men and is the second leading cause of cancer mortality in men (behind lung and colorectal cancer).
13 symptoms of prostate cancer
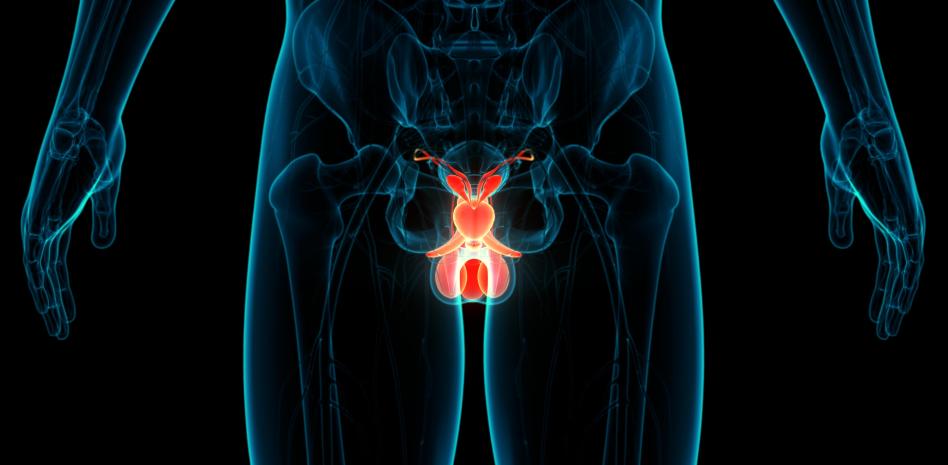
The prostate is a part of the male reproductive system made up of the penis, prostate, seminal vesicles, and testicles. It sits just below the bladder and in front of the rectum, explains the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). It is about the size of a walnut and surrounds the urethra. Its function is to produce the liquid that is part of semen.
Health authorities explain that the symptoms of prostate cancer are different for each person. In some cases, men do not have any symptoms. According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), these are some of the most common signs:
- Frequent urination.
- Weak or interrupted flow of urine, or the need to strain to empty the bladder.
- Urge to urinate frequently at night.
- Blood in the urine.
- Blood in the seminal fluid.
- New set of erectile dysfunction.
- Pain or burning when urinating, which is much less common.
- Discomfort or pain when sitting, caused by an enlarged prostate.
If the cancer has spread outside the prostate gland, you may also experience:
- Pain in the back, hips, thighs, shoulders, or other bones.
- Swelling or fluid buildup in the legs or feet.
- Weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Fatigue.
- Change in bowel habits.