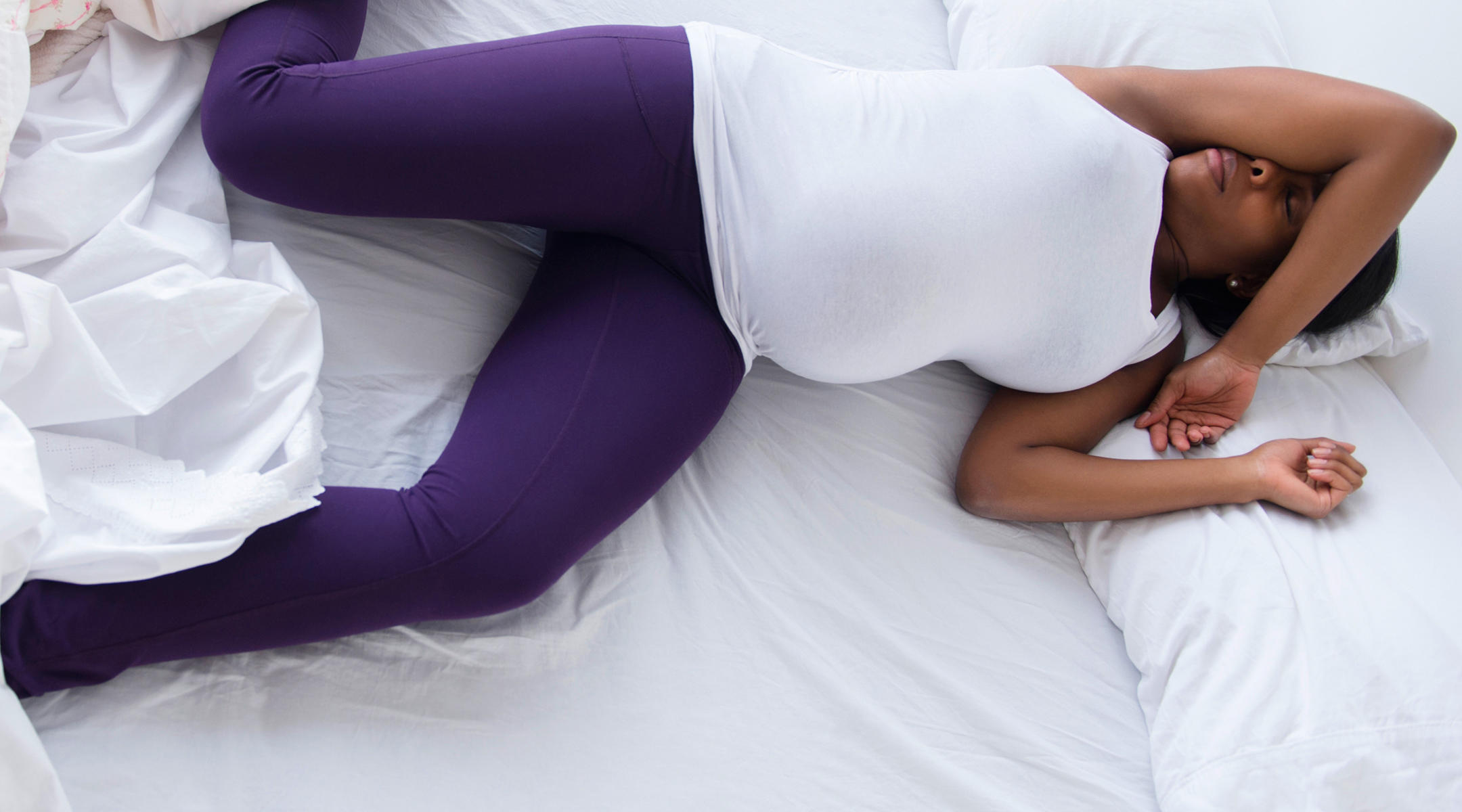
According to the authors of a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, most pregnant women spend about 25% of their sleep in the supine position, which can be a risk factor for the fetus and influence the low birth weight

Due to an exacerbation of breathing disturbed by sleep and oxygen deprivation of the fetus when sleeping on its back.
While positional therapy is a well-accepted way to reduce supine sleep time and increase lateral sleep in adults with sleep-related breathing disorders, there are no previous studies that have examined its use in pregnant women.
The authors of the study, led by Jane Warland, have created a device, called the PrenaBelt, designed specifically for pregnancy.
It is usually a band with spheres on the back that is used to go to sleep. When turning face up, the person feels the spheres and wakes up by the discomfort, changing position.
The results of the study show that the average time of supine sleep was significantly reduced from 48.3 minutes during the night of control to 28.5 minutes during the night of intervention.
An improvement in the maternal and fetal parameters was also observed during the night of intervention, with an increase in the average of the maternal oxygen saturation minimum, less maternal oxygen desaturations and a reduction in the decelerations of the fetal heart rate.
“Our findings suggest that women can sleep comfortably with a device around their waist that prevents them from sleeping on their backs,” Warland explains in a statement.
“Using positional therapy to keep the pregnant mother on her side can reduce supine sleep at the end of the pregnancy, pregnancy and provide maternal and fetal health benefits, with minimal impact on maternal perception of sleep quality and sleep time”.
The study included 25 healthy women during the end of pregnancy (between 32 and 38 weeks of gestation).
During two consecutive nights they were evaluated while they were sleeping at home: one night without intervention as a control and one night while using the PrenaBelt.