An earache is represented by a varied level of pain in the inner ear. Earaches are often caused by a bacterial or viral infection, moving into higher altitudes, or wax buildup.
Earaches are not usually the cause of serious medical conditions, though they can be very unpleasant and painful.
If an earache lasts for longer than 24 hours, it is best to see a doctor. They can check if there is an underlying problem that is causing the pain.
Fever, swelling of the ear, weakness in the face muscles, and dizziness can sometimes occur with an earache. These symptoms may need further medical attention.
Earaches can often be a symptom of larger conditions. These conditions include:
- Swimmer’s ear: This condition occurs when the ear is exposed to too much moisture, usually from swimming. If the ear is damp for a long time, the risk of bacteria growing in the ear increases. When a bacterial infection occurs, it can lead to swimmer’s ear.
- Swollen lymph nodes: The lymph nodes are an important part of the immune system. When there’s an infection, these glands can sometimes become enlarged. As some lymph nodes are found behind the ears, it’s possible that their swelling can cause an earache.
- Upper respiratory tract infection: This is one of the most common viral infections and causes coughing, sneezing, and sometimes earache.
- Headache: The increased pressure that builds up in the head during a headache can sometimes cause pain in the ear.
10 remedies for earache
Even if an earache is part of a larger issue, it is possible to reduce pain with both natural and medical methods. Here are 10 remedies for reducing earache.
1. Ice pack
Holding an ice pack or cold, damp washcloth to the ear for 20 minutes may help numb ear pain and reduce any potential inflammation that is causing it.
2. Garlic
Garlic is a natural remedy for earache that’s been used for thousands of years. Allicin, a compound in garlic, is said to be helpful in fighting bacterial infections that may be causing an earache.
![[garlic]](http://cdn1.medicalnewstoday.com/content/images/articles/312/312634/garlic.jpg)
Garlic has been used as an earache remedy for thousands of years.
Eating raw garlic is said to help reduce ear pain. However, garlic may interfere with antibiotics, so it should only be eaten alongside medical advice. Garlic is also said to be a natural pain reliever.
3. Heating pad
A heating pad or hot cloth held against the ear for 20 minutes may be helpful for temporary pain relief. While cold temperatures may help numb pain and reduce inflammation, a heating pad can relax the muscles and help improve blood flow.
4. Ear drops
Over-the-counter remedies can be successful for some people, especially those that have tried natural methods. Many over-the-counter medications shouldn’t be used by people whose eardrum has ruptured. Some people may also need to check with their doctor to make sure their chosen remedy won’t interfere with any currently prescribed medications.
5. Pain relievers
Pain relievers like ibuprofen can help control pain caused by earache. These medications shouldn’t be used to mask pain, however, especially if the earache is associated with a bigger underlying condition.
6. Sleep in an upright position
Sleeping in an upright position is often advised to help reduce the buildup of pressure in the ear.
7. Chew gum
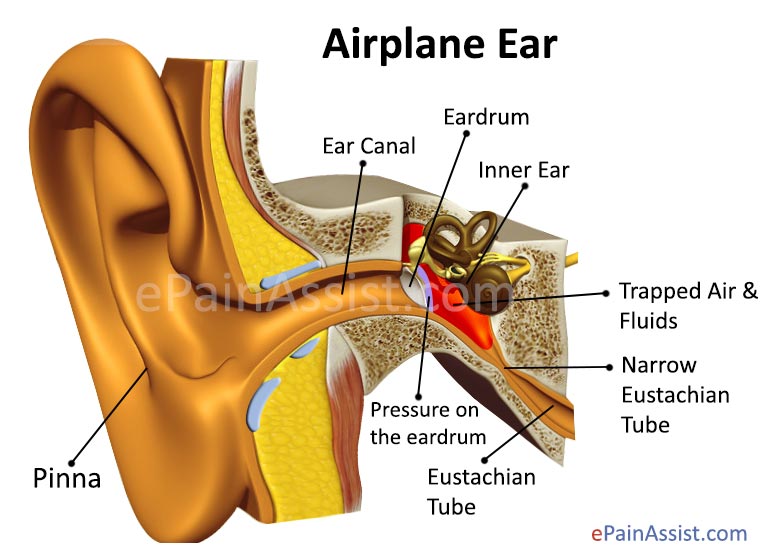
If an earache occurs during or after plane travel or moving to higher elevations, chewing gum may help “pop” the ears and reduce pressure.
8. Distraction
One of the best methods for reducing the feeling of pain, particularly among children, is to distract the mind from the earache. Games, television, or exercise can help reduce attention on earache.
9. Chiropractic
One earache remedy is chiropractic, an alternative health approach. Chiropractic seeks to reduce pain and other health conditions by working with the muscles and bones. It is believed that earache can be caused by the misalignment of the upper neck bones. A chiropractor may be helpful for bringing these bones back “in line,” helping to reduce earache.
10. Myringotomy (ear tubes)
Long-term ear infections are often treated with myringotomy. This is a surgical incision that installs ear tubes into the ears. These tubes help drain fluid and relieve pressure.
Causes of earache
Swimmer’s ear, swollen lymph nodes, and headaches can cause earache but aren’t the only conditions that cause the issue. Additional causes of earache include:
- Earwax buildup
- Temporomandibular joint syndrome (TMJ)
- Ear infection
- Sinus infection
- Tooth infection
- Water or shampoo that gets stuck in the ear
- Pressure changes when entering places of high elevation
Risk factors
There are certain factors that can increase the chance of developing an earache. Some of these factors can be changed. Risk factors for earache include:
- Family history: There may be a genetic factor for persistent earaches. Children with siblings or parents who consistently have inner earache will also experience earache with the same length of time and severity.
- Age: Children are more likely to get earaches than adults. Children 3 years or younger are the most affected age group. This is because a child’s immune system hasn’t fully developed due to their limited exposure to bacteria.
- Weakened immune system: There is a link between long-term weakened immune systems and earaches. Here, earaches are usually the result of a long-standing infection. Improving lifestyle habits, like healthy eating and exercise, may support immune system health. Additionally, washing hands and maintaining good bodily hygiene can be helpful.
- Allergies: People who suffer from allergies are also more likely to experience earaches on a consistent basis. Allergies cause stuffiness in the nose that can block tubes in the ear. This often contributes to buildup in the middle ear and causes increased inner ear pain. Prescribed or over-the-counter allergy medications can be helpful for reducing earache symptoms.
Symptoms of earache
While earache symptoms vary in level of pain severity and duration, there are some symptoms that remain consistent. Symptoms of earache include:
- Ear pain
- Irritability
- Fever
- Crying in infants and young children
Complications may arise if consistent earaches remain untreated. Hearing issues may occur, although they are usually temporary.
Children who regularly have earaches may experience delayed talking due to these hearing issues. This is more likely if these earaches occur before the child learns to talk.
If fluid is allowed to build up in the ear, there could be a rupture of the eardrum. This rupture usuallyEarache prevention
Some of the best prevention strategies for earache are easy to do. Being mindful to keep water and shampoo away from the ears while washing can help to reduce the risk of water-associated earaches.
Drying the ears thoroughly with a dry towel after being in the water can be a great way to prevent excess water from building up. Wearing earplugs while swimming can also be helpful.
For earaches involving infections in children, it’s important to keep children away from others with colds or upper respiratory tract infections. Although not always ideal, it could be helpful for reducing the risk of infection.













